| Risk associated with receiving and executing projects |
- Change of plans, cancellation, suspension, or postponement of projects in the Total Engineering Business after orders are received
- Worsening financial conditions, insufficient project execution capabilities, and defaulting in the portion of operations covered by joint venture consortium partners as comprehensive engineering projects are executed
|
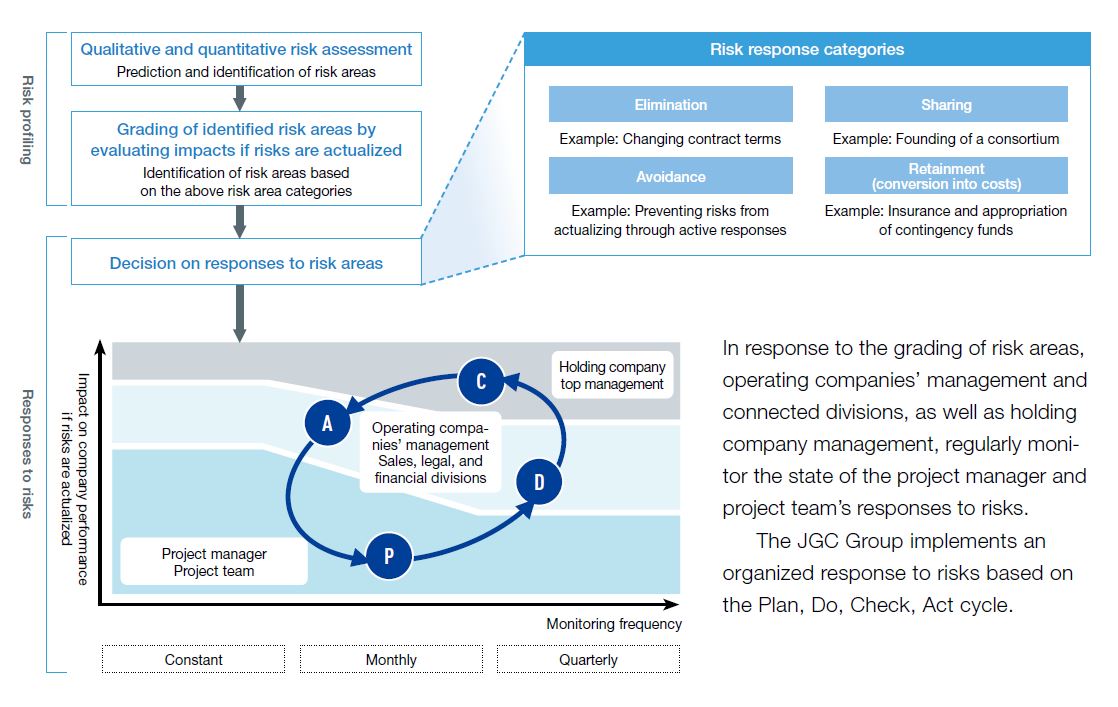
- Specific risk analysis and management by operating companies, monitoring of project progress and profitability
- In addition to the above, as a holding company we will implement the following:
(1) Discuss at Board of Directors’ meetings the aforementioned risks from the estimation and bidding stages for projects that could impact the overall management of the Group.
(2) Review contract negotiation policies prepared by each operating company based on a contract terms policy that consolidates past project experiences for projects that could affect the overall management of the Group.
(3) Conduct partner due diligence to investigate the financial condition and project execution capabilities of partner companies in advance, and take appropriate measures.
|
| Country risk |
- Impact on business activities from political instability, war, revolution, domestic conflict, terrorism, sudden changes in economic policies or conditions, or economic sanctions
|
- Use of trade insurance
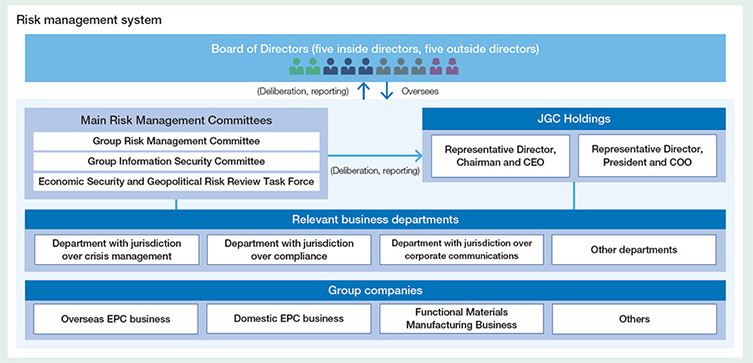
- Collecting, analyzing, and sharing information on country risk for the Group as a whole by the Group Risk Management Committee and Economic Security and Geopolitical Risk Review Task Force.
- Setting reasonable contract conditions with clients, addressing force majeure clauses and regulatory changes
- Strengthening crisis management functions by the Crisis Management Dept.
|
| Risk associated with natural disasters, epidemics, etc. |
- Impact on business activities from natural disasters of unforeseen magnitude such as earthquakes, torrential rain, or typhoons, or from global pandemics such as new strains of influenza
|
- Establishing disaster response procedures, introducing systems to confirm safety, and implementing disaster training
- Gathering information on risk
- Taking necessary measures in response to official requests, confirming safety in accordance with national conditions and regulations
- Setting reasonable contract conditions with clients, addressing force majeure clauses and regulatory changes
- Requesting and discussing with clients any necessary rescheduling or rebudgeting
|
| Foreign exchange volatility risk |
- Impact on sales and profit/loss from sharp fluctuations in foreign exchange rates
|
- Using project contracts denominated in multiple currencies, using overseas procurement
- Issuing orders denominated in foreign currencies, using forward foreign-exchange agreements
|
| Risk of construction worker shortages, substantial wage increases |
- Impact on business activities in the Total Engineering Business from shortages of construction workers or substantial increases in wages
|
- Monitoring and forecasting trends in the construction industry labor force for primary plant markets
- Adopting modular construction techniques to minimize on-site construction
- Working with companies that have extensive track records in local construction
- Addressing this risk in contracts
|
| Risk of substantial increases in fuel, material and equipment costs |
- Increased procurement and transport costs for material and equipment in the Total Engineering Business
- Substantial rises in prices of raw materials or fuel in the Functional Materials Manufacturing Business
|
- Monitoring and forecasting price trends, ongoing efforts to improve forecast accuracy
- Placing orders for materials and equipment early on
- Diversifying suppliers
- Transfers to product prices
- Addressing this risk in contracts
|
| Investment risk |
- Loss from unforeseen circumstances in the investment environment
- Inability to withdraw from investments at the preferred time or in the preferred manner, due to low liquidity or similar factors
|
- Clarifying the significance and purpose of new investment, and making decisions after deliberation by the Board or committees
- Careful selection of new investments
|
| Legal and regulatory risk |
- Restrictions under business laws and regulations such as tax or construction laws, various domestic and international environmental laws, import/export trade regulations including those for security purposes, various laws and regulations to prevent corruption such as graft, laws and principles on human rights protection, or business or investment licenses
|
- Developing, implementing, monitoring, and improving compliance programs and Group policies and rules
- Under the Group-wide Compliance Committee, compliance officers appointed at key Group companies design and implement measures tailored to each company’s specific circumstances
- Special emphasis is placed on establishing rules and providing guidance and oversight regarding bribery prevention measures and compliance with import/export trade regulation.
|
| Information security risk |
- Leaks and loss of information from power outages, disasters, failure, loss, or theft of host computers, servers, or network equipment, external attacks, or virus infections
|
- The Group Information Security Committee identifies Group-wide information security responses, and formulates and deliberates on strengthened measures.
- Security measures such as preventing intrusion by establishing information security policies, adopting antivirus measures, and using encryption
- Information security education, training and practice for executive officers and employees
|
| Risk associated with quality |
- Poor quality of supplies or items procured, recall of delivered products due to defects, liability for damages
|
- Promoting quality management system activities by establishing organizations with jurisdiction over quality assurance
- Using product liability insurance
|
| Risk associated with changes in the macroeconomic environment and social and international affairs |
- Impact on business activities from fluctuating energy prices linked to global recessions
|
- Collecting, analyzing, and sharing information on risks related to changes in the macroeconomic environment and social and international conditions for the Group as a whole by the Group Risk Management Committee and Economic Security and Geopolitical Risk Review Task Force.
- Diversifying our business portfolio by shifting to a Group management structure
- Developing technologies to reduce environmental impact
- Building value chains in collaboration with other companies that possess advanced technologies
|
| Risk associated with climate change |
- Natural disasters at construction and manufacturing sites
- Impact on business activities from lower fossil fuel related investment by clients, or from similar changes to client business itself
- Changes in the business environment such as changes throughout society and industry as the backdrop to climate change issues
|
- Receiving and executing non-fossil fuel, circular economy, and renewable energy projects
- Transforming business areas, business models, and the Group's internal organization in line with the 2040 Vision, our long-term management vision
|
| Risk associated with intellectual property |
- Potential inadvertent infringement of third-party intellectual property rights in countries where it is difficult to understand the intellectual property system or the status of third-party rights
|
- Establishment of a strengthened governance framework for intellectual property management
- Implementing appropriate measures to respect third-party intellectual property rights, and preventing patent disputes, etc.
- Conducting internal education regarding intellectual property, and promoting awareness by disseminating information
- Monitoring third-party intellectual property rights, and identifying, analyzing, and addressing intellectual property risks through collaboration among relevant departments
|