Corporate Governance
Basic Stance
The JGC Group remains aware that, in line with our purpose of "Enhancing planetary health," sound governance is the foundation for management in pursuit of higher medium- to long-term corporate value and sustained growth. We are therefore strengthening our corporate governance, which we view as a priority material issue.
Our central mechanism for corporate governance is the Board of Directors. Its governance structures, functions, and roles are continuously reviewed, with Board effectiveness analyzed and assessed each year as we seek progress through steady improvement.
In shareholder and investor engagement, we take a proactive stance in highly transparent information disclosure, and viewpoints from this dialogue are applied to strengthen governance and management. In regulatory compliance and other matters essential to appropriate corporate governance as well, our purpose and values call on each employee and officer to maintain high ethical standards in everything they do, so that the Group as a whole works to enhance medium- to long-term corporate value and achieve sustained growth.
Outline of Corporate Governance System
JGC Holdings maintains a board of directors and an audit and supervisory board. The JGC Group has adopted a holding company structure under which operating companies pursue the Group's core business.
Outline of Corporate Governance System
| Body | Purpose | Meetings | Members | Head of organization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Board of Directors |
|
Generally monthly |
Seven directors (including four outside directors) Five auditors (including three outside auditors) (For fuller discussions, others also attend as needed, such as operating company officers, executive officers in charge of certain areas, and those in relevant divisions) |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato |
| Nominating and Remuneration Committees |
|
Annually (and as needed) |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka Three outside directors*
|
Nominating Committee: Outside Director Shigeru Endo Remuneration Committee: Outside Director Masayuki Matsushima |
| Audit & Supervisory Board |
|
Generally monthly |
Five auditors (including three outside auditors) | Full-time Audit & Supervisory Board Member Yasumasa Isetani |
| Group Steering Committee |
|
Generally monthly |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka Auditors (rotating) (Consists of members such as group company officers appointed by the chairperson) |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato |
| Sustainability Committee |
|
Generally annually |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato Consists of members proposed by presidents and chairpersons of Group companies and approved by the president of their company |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato |
| Group Investment and Loan Committee |
|
Generally monthly |
Standing members: Seven directors, executive officers, and auditors of the holding company and Group companies. Non-standing members: Three executive officers of the holding company may attend, depending on the agenda. |
Chairman and CEO Masayuki Sato |
| Group Risk Management Committee |
|
Generally bi-annually |
President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka Members appointed by the chairperson, and members appointed by the chairperson based on recommendations by the presidents of each operating company |
President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka |
| Group Information Security Committee | Understands the status of information security measures across the Group as a whole, and plans and discusses cross-company adjustments and enhanced responses among Group companies | Generally bi-annually | President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka Members from Group companies nominated by the chairperson and vice-chairperson |
President and COO Tadashi Ishizuka |
| Accounting Auditors |
|
|||
Corporate Governance System
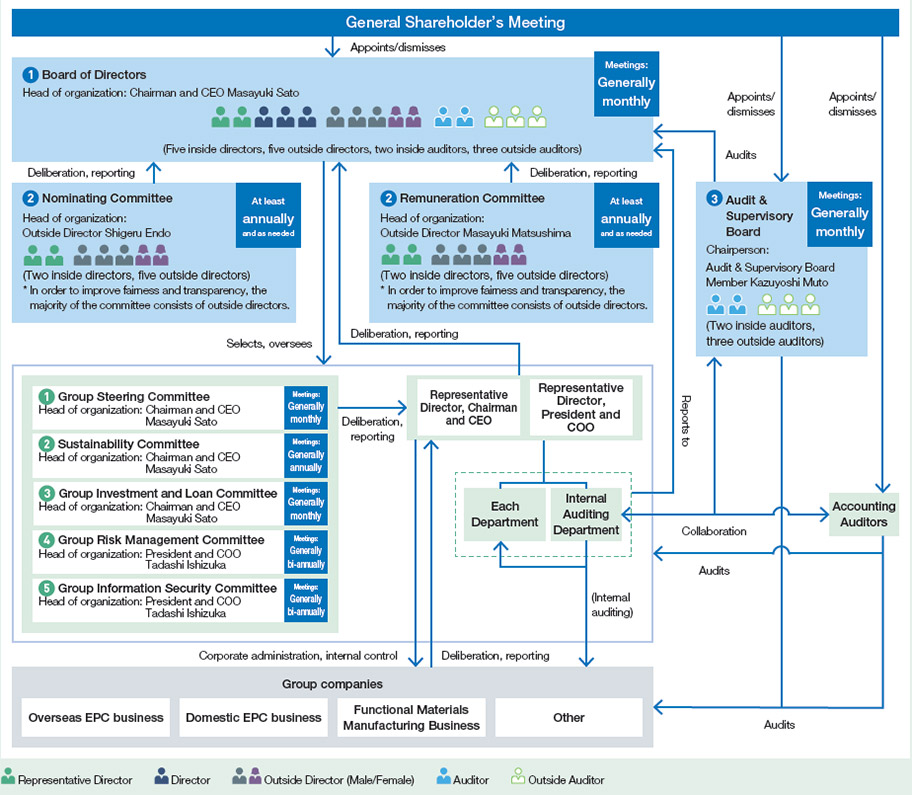
Separating management from execution provides greater clarity on roles and responsibilities of the holding company and operating companies. The holding company's role is to formulate management policies and oversee the operating companies from a medium- to long-term Group perspective. Operating companies apply Group management policies and strategies to respond flexibly and rapidly to market characteristics and seek further business expansion. This is intended to maximize corporate value and ensure optimal allocation of management resources for the Group as a whole while enhancing transparency of corporate management and strengthening overall Group governance. Committees have been established to deliberate key Group matters, and an executive officer system has been introduced to ensure efficient managerial decision-making and execution.
Improvement Status of Internal Control System
JGC Holdings' Board of Directors determines the basic principles of the internal control system and revises them as necessary.
【Improvement Status】
- 1.The Internal Auditing Department monitors, evaluates, and improves the effectiveness of the internal control systems of JGC Holdings and the JGC Group and conducts separate audits as necessary
- 2.Rules of Management Authority regulate the duties and authority of each role, and clarify the system of responsibilities in corporate management and business execution
- 3.Management rules for Group companies have been formulated and implemented to ensure efficient and appropriate operations across the Group
About JGC's Response to the Corporate Governance Code
We implement all principles laid out in the Corporate Governance Code and provide disclosure according to all 14 general principles, and supplementary principles required by the Tokyo Stock Exchange as stipulated in the revised Corporate Governance Code of June 11, 2021, and are making steady efforts to further solidify our corporate governance.
A Corporate governance report is available on the JGC Group website. (Only in Japanese)
- *CPAs Takemitsu Nemoto, Atsushi Nagata, and Takashi Inoue of KPMG AZSA LLC audit JGC accounts. Auditing support is provided by nine other CPAs and 16 assistants.
Board of Directors
Board Functions
The Board of Directors is responsible for decision-making on medium- to long-term group strategy and issues, and it provides oversight regarding business execution of the Group companies. Board composition is intended to enable effective and efficient execution of these functions.
Basic Policy on Board Composition and Diversity
From the standpoint of further enhancing discussions on medium- to longterm group strategies and issues and of strengthening oversight regarding business execution of the Group companies, the board consists of the following members.
- 1.Consists mainly of directors with broad experience in business markets and directors with a high level of knowledge and expertise in EPC operations, which is the primary Group business.
- 2.Independent outside directors are appointed in order to incorporate outside perspectives in management, with the expectation that these directors will provide objective advice to the board and fulfill oversight functions from an independent viewpoint.
As a matter of policy respecting the importance of diverse perspectives, members are appointed not solely based on professional experience and expertise but also on competence, regardless of nationality, race, or gender.
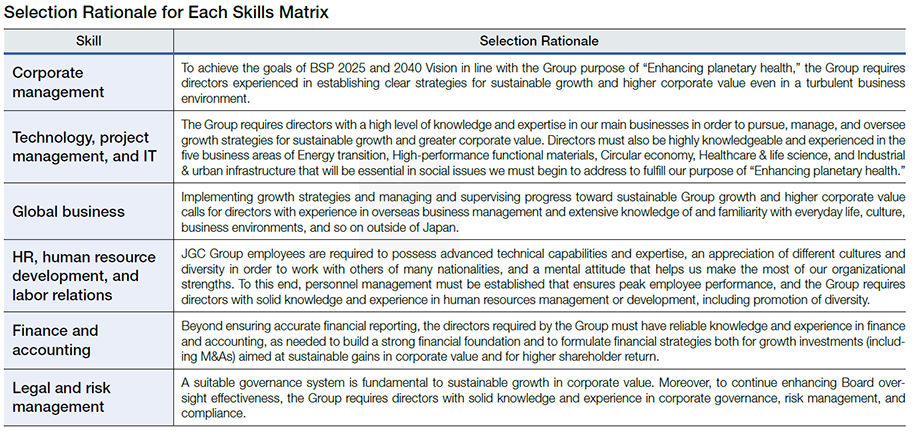
Skills Matrix for Directors and Auditors
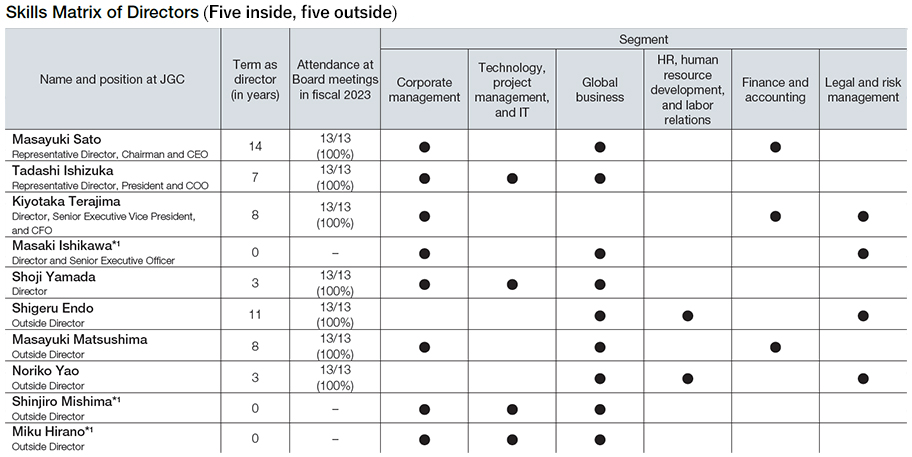
- *1Appointed at the General Shareholders’ Meeting held in June 2024.
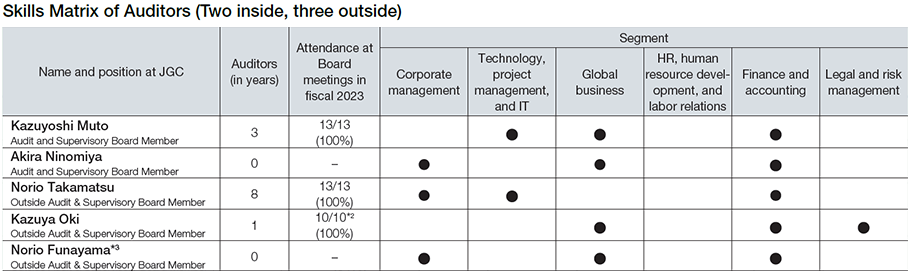
(Notes)
Selection rationale for each skills matrix is shown below. The above list is not exhaustive or prescriptive, which indicates disciplines where directors and auditors can further demonstrate their expertise, not all disciplines in which each director and auditor excels. In addition, ESG-related fields are positioned as an expected role required of all directors and auditors, and are therefore not listed as a separate item in the above table.
- *2Attended the Board of Directors’ meeting following the General Shareholders’ Meeting held in June 2023.
- *3Appointed at the General Shareholders’ Meeting held in June 2024.
Policies and Procedures for Senior Management Appointment and Dismissal
Appointment process
Appointment of senior management and nomination of candidates for directors
- 1.Deliberations of the Nomination Committee, which consists of a majority of outside directors and is chaired by an outside director, are focused on the following items.
- (1)Qualities such as character and views
- (2)Senior management and inside directors: Qualities such as experience, performance, and management capabilities, as defined in succession planning
- (3)Outside directors: Qualities such as independence and expertise
- 2.After comprehensive deliberation by the Nominating Committee, a decision is made by the Board.
- (1)Appointment of senior management and nomination of director candidates follows this process and involves ample discussion before decisions are made, with the understanding that these individuals may one day be candidates to succeed the CEO.
Dismissal process
Dismissal of senior management
In the event of any of the following, the Board decides on dismissal after deliberation by the Nominating Committee.
- (1)Wrongdoing, impropriety, or breach of faith
- (2)Violation of laws or articles of incorporation
- (3)Loss of the qualities and capabilities initially required for appointment
Succession plan
The following succession plan in place informed by discussions of the Nominating Committee and Board is beginning to be initiated, reflecting the Group's recognition of the importance of succession planning in sustainable growth of corporate value.
Purpose
- Toward attainment of BSP 2025 and the 2040 Vision, and for lasting enhancement of corporate value beyond this, we recognize the necessity of appointing optimal directors and executive officers for the current business environment and management strategies.
- Based on the business environment and management strategies, the plan clarifies the knowledge, experience, abilities, and personal qualities sought in top management, guiding development and selection of the Group's next leaders and enabling continuous appointment of these leaders whenever needed.
Stance on leadership criteria
- In fiscal 2019, leadership criteria were determined through talks with current top management facilitated by a third-party organization, and future needs in leaders were defined from a medium- to long-term management vision.
- These criteria are classified on minimum essential attributes and ideal attributes (three-level scale), and candidates are assigned to groups with specific level requirements.
Stance on succession planning
- The basic stance taken on succession planning involves defining leadership criteria, selecting several individuals for near- and far-term candidate groups, providing opportunities to develop required attributes and gain experience, and monitoring progress each year as candidates are groomed over the medium to long term.
- In line with the above approach, educational programs for near- and far-term candidate groups are enhanced and built upon through measures such as sending candidates to external educational and training programs, inviting external lecturers to give ongoing lectures, and providing opportunities for ongoing discussions.
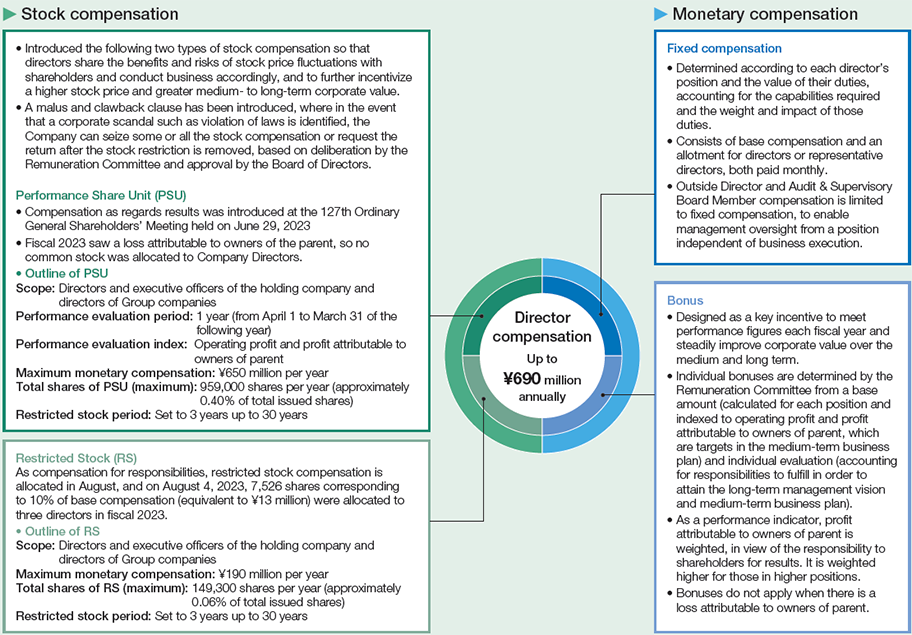
Director Compensation
Policy on Determining Director Compensation Amounts or Calculation Methods
Basic Policy, General Share-Holders' Meeting Resolutions
- Under a basic policy to secure the management personnel needed for greater global competitiveness and higher medium- to long-term corporate value, a resolution made at the 113th general shareholders' meeting on June 26, 2009, set maximum annual director compensation at ¥690 million, with maximum auditor compensation at ¥88 million.
- As for the policy on determining the amount, calculation, and breakdown of compensation for individual directors, compensation shall not exceed the range resolved at the general shareholders' meeting, and details are discussed in advance by the Remuneration Committee (which consists of a majority of outside directors and is chaired by an outside director), whose report is considered by the Board to reach a decision.
Process for Determining of Compensation
- To ensure fairness, transparency, and consistency with this decision policy, decisions by the chairman and CEO reflect the results of comprehensive deliberation by the Remuneration Committee on evaluation of individual directors and the amount of remuneration.
- The compensation for individual directors within the range set at the general shareholders'meeting is at the discretion of the chairman of the Board, who as the Company's CEO is most familiar with the duties and responsibilities of each director, their performance, and the extent to which this performance contributes to higher corporate value.
- The Board has determined that final decisions have been consistent with this policy, and in making this determination, the Board has been informed of a summary and results of Remuneration Committee deliberations, as well as final decisions by the chairman and CEO.
Compensation mix and details
- Inside directors, excluding outside directors, receive compensation comprising monetary compensation and stock compensation, where monetary compensation comprises fixed compensation and bonuses, and stock compensation comprises restricted stock and performance share units.
- The compensation mix is designed to provide a higher proportion of variable compensation (bonus and stock compensation) for higher performance and rank.
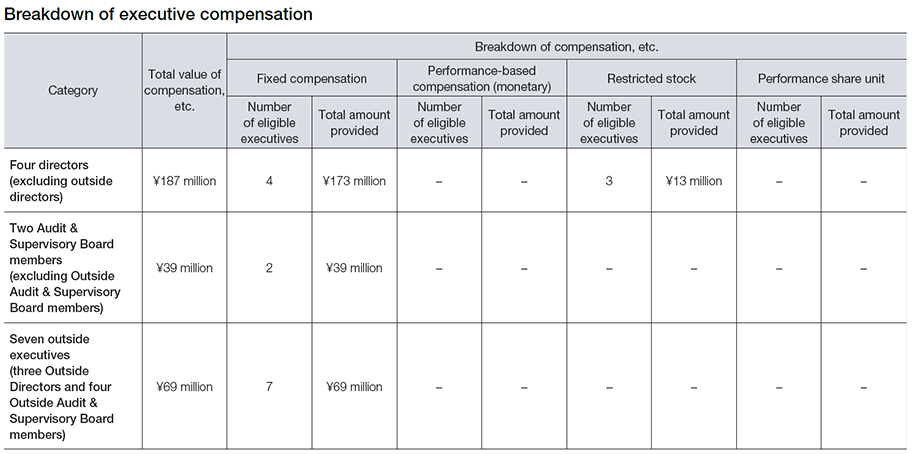
Breakdown of Executive Remuneration
(Notes)
- 1As of the end of fiscal 2023, there were seven directors (including three outside directors) and five auditors (including three outside auditors).
- 2The performance-based compensation (monetary) and performance share unit above did not achieve the performance evaluation indicators, and so were not granted.
- 3Since our Company has no executives with total remuneration of \100 million or more, individual compensation is not disclosed.
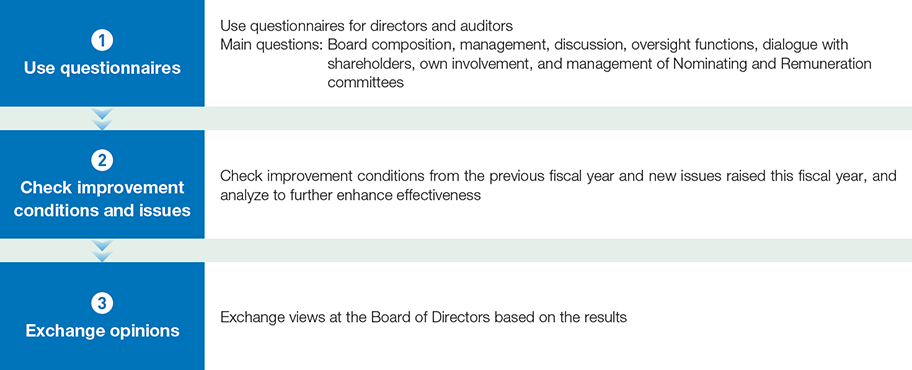
Board Effectiveness Evaluation
Board effectiveness is analyzed and evaluated annually, efforts toward improvement are reviewed, and issues linked to further gains in effectiveness are discussed by the Board in pursuit of continuous improvement. Presented below is a summary of the process for evaluating Board effectiveness in fiscal 2022, the state of initiatives based on the Board evaluation results of the previous year (fiscal 2021), and future response policy based on these evaluation results.
Process
Evaluation results
Survey analysis and evaluation has indicated that the Board is functioning appropriately and effectively in its current state. Details of the evaluation results are as follows.

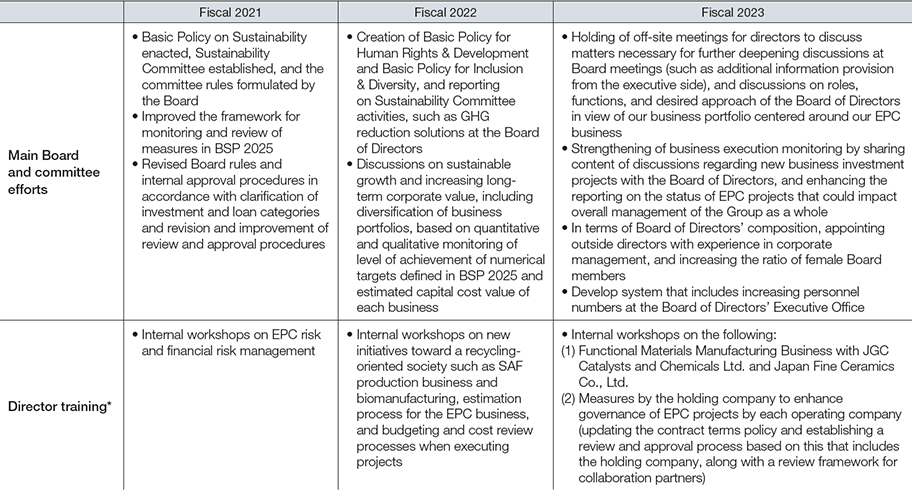
Main Efforts to Date for Improving Board Effectiveness
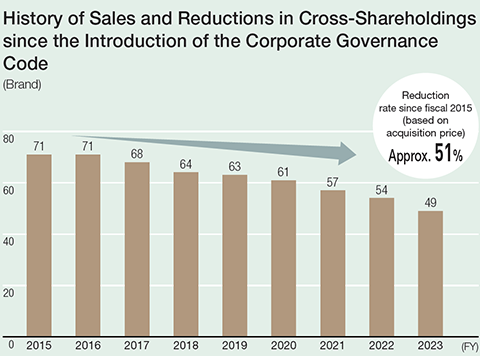
Cross-Shareholdings
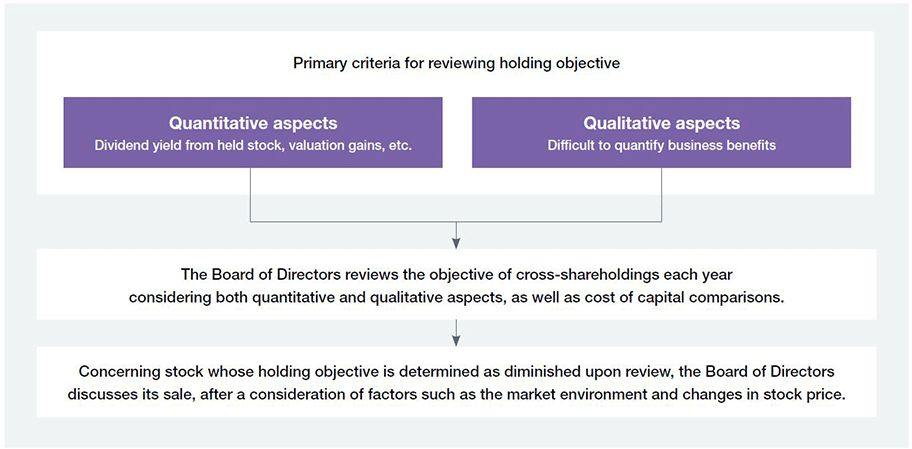
1. Purpose
The Group refrains from cross-shareholdings except in cases where maintaining and strengthening relationships with clients and business partners will contribute to higher medium- to long-term corporate value for the Group. Each year, the Board of Directors reviews the significance of maintaining each cross-shareholding, and both qualitative and quantitative aspects are reviewed. Quantitatively, TSR (total shareholder return) and ROE are checked for each company, as well as whether business advantages are commensurate with the cost of equity. Sale of shares deemed to have lost their significance is investigated accounting for the market environment and changes in stock prices.
2. Basis for exercising voting rights
In exercising voting rights for cross-shareholdings, advantages and disadvantages are weighed based on whether the decision will contribute to sustained growth of the company involved, and thus, higher group corporate value over the medium to long term.