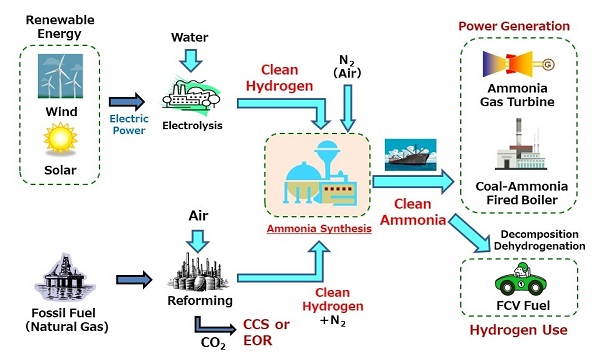
Clean Ammonia Synthesis - Clean Energy Carrier
Clean ammonia includes blue ammonia, which captures and stores CO2 emitted from fossil fuels, and green ammonia, which is derived from renewable energy. JGC is developing green ammonia production technology. The use of this ammonia as fuel in thermal power plants or boilers and industrial furnaces aims to contribute to reductions in CO2 emissions. Under atmospheric pressure, ammonia can be liquefied at the relatively mild temperature of minus 33 degrees Celsius, making it easier to store for long periods and transport than other hydrogen energy carriers, for which it has been attracting attention.
- *Energy Carriers
A method by which hydrogen, which is difficult to store or transport over long distances, can be made easier to handle by changing it to liquid form.
Features
- Ammonia synthesis technology is suitable for synthesizing low pressure hydrogen produced from renewable energy
- Highly active ammonia synthesis catalyst at a lower temperature and pressure than current iron-based catalysts
- Systems that enable optimum operation, even with fluctuating renewable energy sources
- CO2-free fuel (fuel that does not emit CO2)
- Ammonia is easy to transport and store
Applications
- Regions with a wealth of inexpensive renewable energy
- Regions with surplus renewable energy
Development Status
- Completed a demonstration test of ammonia synthesis at the Fukushima Renewable Energy Institute, AIST.

- Launched a green chemical demonstration project with Asahi Kasei under the NEDO Green Innovation Fund Project.
Background
As a global issue, we need to realize energy diversification and a low-carbon society, aiming for environmental preservation and a sustainable society. Hydrogen energy is expected to play an important role in this process, since hydogen does not release any CO2 during combustion.
To utilize hydrogen energy, there are still issues with regard to safety, economic feasibility, and efficient transportability and storage. To solve these issues, Energy Carriers, such as Ammonia, Liquid hydrogen, and Organic hydrides, have been developed. Among these Energy Carriers, Ammonia contains the highest density of hydrogen, has ease of liquefaction, and able to be directly combusted without releasing CO2. Also, Ammonia is utilized as fertilizer and chemical feedstock, and its supply chain is already established commercially in the world. This is the reason why Ammonia has advantages over the other Energy Carriers.
Status of Ammonia Related Technology Development and Future Market as Energy Carrier
"Hydrogen General Strategy"published in December 2017 stated to aim at partial introduction of ammonia as a fuel into existing coal fired boilers around 2020, and commercial utilization of Ammonia into existing coal fired boilers around the middle of the 2020s.
Since 2014, the Cabinet Office, in its "Cross Ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP)," has expressed Japan's intention to create an innovative low-carbon, hydrogen-energy economy by the year 2030 and to take the lead in hydrogen related industries on the world market through its "Energy Carriers" research. JGC participated in the SIP "Energy Carriers" research titled "Development of Ammonia Synthesis Process from CO2 free Hydrogen."
In addition, JGC has joined the Clean Fuel Ammonia Association which has been established to promote ammonia as an energy carrier, and has been supporting work in the area of clean Ammonia supply especially.
- *Cross Ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program
The Overall technical research and development Innovation Council is not bound by the traditional sectionalism of individual ministries and seeks new paths toward achieving innovation and technical progress.
Further, in October 2020, the "Interim Report by Public-Private Council for the Introduction of Ammonia as a Fuel" was established, which JGC is participating as a member. The "Public-Private Interim Report on the Introduction of Ammonia as a Fuel" released in February 2021 also presented a roadmap for the introduction of ammonia as a fuel, with a target of 3 million tons per year by 2030 and 30 million tons per year in Japan by 2050.
Aiming at High Efficiency Synthesis and Stable Production of Green Ammonia
To utilize ammonia as fuel in power generation, ammonia needs to be "CO2 free Ammonia," and CO2 emission during clean Ammonia production shall be minimized as far as possible. The ideal way to produce such ammonia is the synthesis of hydrogen produced from renewable energy by water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from air.
At present, ammonia synthesis conditions are at high temperature and pressure in the presence of an Fe-based catalyst in what is called the "Haber-Bosch Process." However, the hydrogen produced by the use of renewable energy from water through electrolysis is at low pressure. For the use of the "Haber-Bosch Process," high temperature/high pressure condition is necessary to produce ammonia, meaning that the hydrogen needs to be compressed to a high pressure ratio, and the energy efficiency of the process is decreased. To overcome this problem, it is necessary that high efficiency catalyst and its process under lower temperature/lower pressure conditions than the "Haber-Bosch Process" have been developed.
Among renewable energy as feedstock, solar power and wind power fluctuate greatly in the short, medium, and long term. Hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water based on the electric power, and the hydrogen produced also fluctuate greatly according to the power source used. In contrast, downstream ammonia synthesis plants cannot cope with such major variations and therefore it is necessary to design facilities and operating systems that can deal with such problems.
Outline of Current Research and Development
Since 2014, JGC, based on its evaluation of the use of ammonia as an energy carrier has participated in the SIP "Energy Carriers" research title "New Catalysts and Process for Producing Ammonia and the Use of Hydrogen Produced Through the Electolysis of Water by Renewable Energy for the Production of Ammonia."
JGC, together with the AIST and the National Institute of Technology, Numazu College as well as our subsidiary, JGC Catalysts & Chemicals Ltd., has done research and experimentation with support and catalysts and developed catalyst production processes through which a catalyst that will allow the efficient production of ammonia even under low temperature/low pressure conditions can be used.
Responding to the successful development of the new catalyst for producing ammonia, JGC constructed a demonstration plant for its use at the the Fukushima Renewable Energy Institute, AIST in Koriyama-city, Fukushima-prefecture, which is capable of producing ammonia at the rate of 20 kg per day. The demonstration plant was operated.
With a view to developing methods for the efficient and stable use of ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier, JGC plans to operate the demonstration plant with hydrogen produced through the electrolysis of water using renewable energy.
As a next step, JGC, together with Asahi Kasei Corporation, has been awarded a Green Innovation Fund project from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) to develop a “"Large-scale Alkaline Water Electrolysis System Development and Green Chemical Plant Demonstration" and demonstrate a green chemical plant. In this context, JGC is collaborating with Asahi Kasei to develop an integrated control system that controls the hydrogen supply and optimizes the operation of a process that uses hydrogen derived from fluctuating renewable energy sources as feedstock.
The technology developed is expected to be applied to methods of storing and utilizing surplus renewable energy that cannot be connected to the grid or off-grid renewable energy as an ammonia.
Prospective
JGC is aiming to supply clean Ammonia expected to be introduced into power generation plants in the mid-2020's, as stated in the "Hydrogen General Strategy." And JGC is also conducting feasibility studies to supply blue Ammonia to Japan, in a scheme in which ammonia is produced from natural gas and CO2 produced in the reforming process is utilized for EOR (Enhanced Oil Recovery) overseas and transported to Japan by sea freight.
It is also expected that green Ammonia production from renewable energy will be commercially introduced in the late 2020s. To realize this scenario, JGC will continue demonstrations to establish an efficient and stable ammonia synthesis method and technology from renewable energy.
Overview of Clean Ammonia Supply Chain