Wet Oxidation Process for High Dose Resin
Wet Oxidation Process
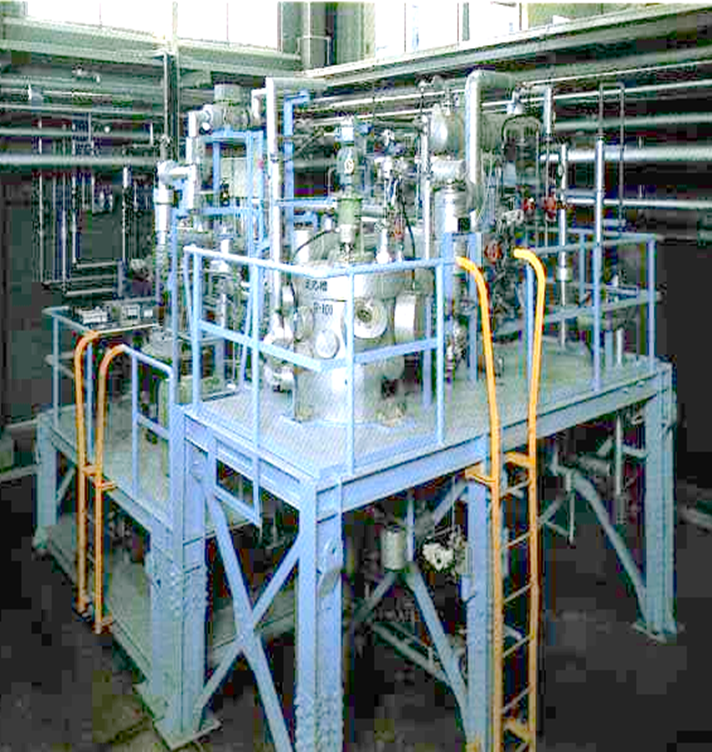
The wet oxidation process is used to mineralize and reduce the volume of high-dose ion exchange resins (high-dose resins) containing radioactive materials by decomposing organic materials into water and carbon dioxide gas in an aqueous solution. Hydrogen peroxide is supplied in the presence of a catalyst (Fe, Cu, etc.) to decompose high-dose resins at 100°C under normal pressure.
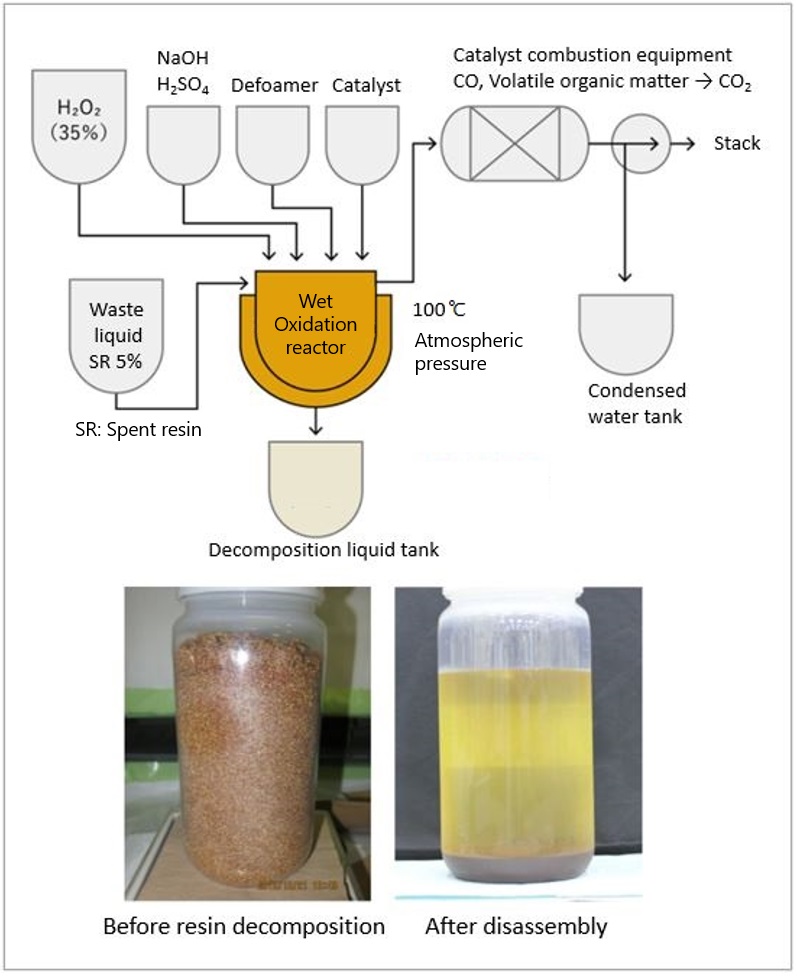

Features
- High-dose resins can be reduced in volume and mineralized
- Mild operating conditions (Normal pressure, 100℃)
- Simple equipment configuration and easy maintenance
- Compact exhaust gas facility compared to high-temperature treatment systems
- Almost no transfer of radioactive materials into the gaseous phase
- After treatment, the decomposed liquid can be transferred through piping.
Applications
The wet oxidation process is suitable for the decomposition of the following organic materials generated at nuclear facilities
- High-dose resins (Granular resins, Powdered resins)
- Filter sludge
- Chelating agents
Experiences
- Demonstration tests of actual waste decomposition at domestic nuclear power plants
- Chelating agent-containing wastewater treatment facilities for U.S. electric power facilities