Investigation for Cause of Damage and Assessment of Remaining Life
Providing a Series of Damage Cause Investigation and Life Diagnosis through Field Investigation, Analysis and Countermeasure Proposal.
Outline
Since the 1980s, JGC has investigated a total of more than 800 damage cases to identify causes of damage through destructive testing of damaged samples, covering not only static equipment and piping, but also rotating equipment and its parts in various industries. By investigation, JPI identifies causes of damage and make studies and provides recommendations on the following:
- 1. Measures to be taken to prevent the same or similar damage
- 2. Emergency and permanent measures to be taken on damaged equipment
- 3. Inspections to be conducted on other undamaged facilities such as equipment and piping being used under similar operating conditions
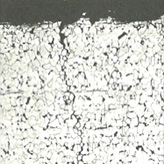

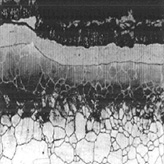
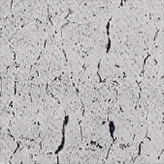
Utilizing Expertise and Years of Experience to Provide
Services that Meet Client Needs
Industrial plants, equipment and piping are subject to creep damage, fatigue damage and corrosion as they are being used. Factors contributing to such damages can stem from their design, materials or environments in which they are being operated. To prevent recurrence of such damages, it is essential to accurately identify the causes. JGC conducts inspections and analyses to correctly identify causes of damage, taking full advantage of the know-how fostered from past experiences.
Technology to Assess the Remaining Life of Damaged
Equipment and Piping - Assessment of the Remaining
Life of Creep Damage
To assess the remaining life of creep damaged plant, three methods are available. According to their respective features, they are applied to JGC's assessment of the remaining lives of plants as follows:
- Destructive Method
- To assess the remaining life of plant, using the Larson-Mirror parameter of heating furnace tube by creep rupture testing.
- Nondestructive Method
- To assess the remaining lives of equipment and piping using A Parameter method.
- To assess the remaining life of the heating furnace tube by measurement of its circumference and the microstructure method comparing with the standard microstructure changes obtained in long-term laboratory test.
- Analytical Method
- To assess the remaining life of the heating furnace tube using the remaining heater tube life estimation calculated based on the total accumulated life fractions.
Comprehensive Investigation from Inspection at Site
to Analysis and Assessment
Utilizing long years of its know-how, JGC plans and conducts inspection for petroleum refining and petrochemical creep damages, followed by assessment and analysis thereon.